CDC Link
This page gives an overview of the CDC single-carrier link, which is provided
to assist with completing the CDC design project. Code for the link can be
found in the gr-elen90089 git repo.
Content
Overview
The CDC link is a modified version of GNU Radio's packet transmission example.
In particular, modifications were made to provide the following functionality.
- Mechanisms for dynamic control of the bladeRF
- Runtime adaptation of the modulation order (e.g., switching between BPSK, QPSK, etc.)
- Improved performance and stability by fixing a number of obscure bugs in the existing GNU Radio example.
Two example GRC flowgraphs, a software loopback and a hardware loopback, demonstrate how to create and configure the link.
./examples/cdc_packet_loopback.grc./examples/cdc_packet_hw_loopback.grc
The CDC link is composed of three main functional blocks that implement a single carrier pulse modulation PHY and skeleton MAC layer.
The Tx/Rx PHY blocks are hierarchical blocks composed of standard GNU Radio C++
signal processing blocks along with some custom C++ blocks in the gr-elen90089
OOT. The custom blocks are modified versions of existing GNU Radio blocks.
Note: This page provides a basic overview of individual blocks in the CDC link. Additional information can be found in documentation of the
gr-elen90089OOT. To view this documentation after building and installing the OOT, open a web browser on the CDC Ubuntu VM and navigate to the following location: file:///usr/local/share/doc/gr-elen90089/html/index.html
Packet MAC Tx
The Packet MAC Tx is implemented as a python block found at the following location:
./python/packet_mac_tx.py
The block has the following configuration parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| payload_bps | Bits-per-symbol of payload constellation, i.e., sets the constellation used to modulate PDU data bytes. Supported modulations include: {1: BPSK, 2: QPSK, 3: 8-PSK} |
| Tx Frequency | Sets the transmit frequency of the bladeRF |
| Tx Gain | Sets the transmit gain of the bladeRF |
The block is currently a simple pass through block that receives a data PDU on its input, updates the PDU's metadata dictionary, and then passes the PDU to the PHY Tx for modulation. The following entries are added to the metadata dictionary of the PDU.
-
bps: bits-per-symbol of the payload constellation -
freq: bladeRF transmit frequency -
gain: bladeRF transmit gain
These metadata entries will be converted to stream tags within Packet PHY Tx.
The bps parameter is then used by downstream blocks to configure the payload
modulation constellation (BPSK, QPSK, etc.). The freq and gain parameters
will prompt the bladeRF to update its transmit frequency and gain just prior to
transmitting this packet. See gr-bladeRF-cdc's
Stream Tag Interface
for more information on how this process works.
The Packet MAC Tx is a very basic skeleton of a MAC layer which you can update for your DSA application.
Packet PHY Tx
The Packet PHY Tx block is a GRC hierarchical block that implements packet- based pulse modulation. The GRC file for this block can be found at the following location.
./examples/packet_phy_tx.grc
The block has the following configuration parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Excess BW | Excess bandwidth of RRC transmit pulse-shaping filter. |
The hierarchical block is composed of the following subblock arrangement.
pdu in > [Async CRC32] > [Protocol Formatter] > [FEC Async Encoder]
> [CDC Symbol Mapper] > [Burst Shaper] > [Polyphase Arbitrary Resampler] > iq outFunctionality for these subblock is as follows.
Async CRC32: Appends a 32-bit (4 byte) cyclic redundancy check (CRC) code to the payload data that is used for error detection at the receiver.
Protocol Formatter: Generates a PHY layer header for transmission at the start of the packet burst. See Header Format CDC below.
FEC Async Encoder: Applies dummy forward error correction (FEC) to the packet header. Dummy here means no code bits are added and this block is just a placeholder for potential channel coding of the packet header.
CDC Symbol Mapper: Maps the header and payload bytes to symbols using independent constellations for the header and payload. See CDC Symbol Mapper below.
Burst Shaper: Prepends phasing symbols to the beginning of the transmit burst along with an amplitude ramp up and ramp down. See Burst Shaper.
Polyphase Arbitrary Resampler: upsamples symbol stream and applies RRC transmit pulse shaping. See Polyphase Arbitrary Resampler
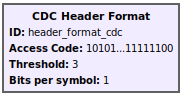
Header Format CDC
The PHY layer header generated for the CDC packet link is used to communicate important configuration information for use by the receive PHY. It includes the following fields.
- access code (64 bits): Training sequence delimiting the beginning of a transmission burst.
- counter (16 bits): Packet sequence number incremented for each newly transmitted packet
- pktlen (16 bits): Payload length in number of bytes. Used along with bps by receiver to determine how many payload symbols are present in a burst.
- bps (8 bits): Bits-per-symbol of payload constellation
- crc (8 bits): Cyclic redundancy check over header fields (counter, pktlen, bps) used by the receiver to check integrity of decoded header
# Mapping of fields in CDC Header Format
| 0 - 7 | 8 - 15 | 16 - 23 | 24 - 31 |
| access code |
| access code |
| counter | pkt_len |
| bps | crc |CDC Symbol Mapper
This block takes in the header and payload PDUs for a given packet, maps them
to each to constellation points, concatenates the resulting symbols (header
symbols followed by payload symbols), and then streams them out on its output
port. The header constellation is specified by the Header Constellation
parameter and is generally intended to be static while running the link. The
payload constellation is specified by the bps entry in the metadata
dictionary of the payload PDU. This metadata item is added by the
Packet MAC Tx block, allowing for the payload constellation
to be changed on a per packet basis.
Packet PHY Rx
The Packet PHY Rx block is a GRC hierarchical block that implements packet-based pulse demodulation. The GRC file for this block can be found at the following location.
./examples/packet_phy_rx.grc
The block has the following configuration parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Excess BW | Excess bandwidth of RRC matched filter. |
The hierarchical block is composed of the following subblock arrangement.
iq in > [CDC TS Correlator] > [Mult Tag Value] > [Symbol Sync] > [Header/Payload Demux]
hdr > [CDC Costas Loop] > [Constellation Decoder] > [Protocol Parser]
pld > [CDC Costas Loop] > [CDC Constellation Decoder] > [FEC Async Decoder]
> [Async CRC32] > phy_sdu outThe first common portion of the receive chain includes the following.
CDC TS Correlator: Searches for the packet training sequence and tags the input stream when found. See CDC TS Correlator below.
Mult Tag Value: Performs single-tap equalisation using the LLS channel
estimate, chan_est, from the CDC TS Correlator to invert the wireless
channel.
Symbol Sync: Performs matched filtering and symbol timing recovery
using an ML timing error detector and polyphase filterbank interpolation. The
time_est parameter estimated by the TS Correlator block initialises the
fractional timing offset of this block. See
Symbol Sync.
Header/Payload Demux: Separates the header and payload symbols for processing. The header must be decoded first to determine the number of payload symbols and payload constellation. These details are fed back from the header decoder chain to this block. See Header/Payload Demux.
The subsequent header decoding chain includes the following blocks.
CDC Costas Loop: Tracks the carrier phase and frequency offset of the received header symbols. Note for the CDC link, the channel equalisation approach removes any phase ambiguity at the start of each packet burst. See CDC Costas Loop below.
Constellation Decoder: Performs hard decision slicing of the header symbols to the header constellation and then demaps symbols to bits. See Constellation Decoder.
Protocol Parser: Searches for access code/training sequence within received header bits and parses header fields once found. Threshold determines the number of incorrect bits that can occur when declaring the access code to be found.
The payload decoding chain includes the following blocks.
CDC Costas Loop: Same as for header decoder chain except the constellation
used to determine the phase error of each symbol is updated by bps tags found
in the symbol stream. See CDC Costas Loop below.
CDC Constellation Decoder: Slices received payload symbols to constellation
points where the constellation used is updated by bps tags found in the
received symbol stream. This is needed to support changing payload modulation
on a packet-by-packet basis.
FEC Async Decoder: Dummy FEC decoding of received payload bits. This block is currently present to convert the output format of the CDC Constellation Decoder block from soft bits (real valued) to packed bytes. With appropriate modifications to the transmitter it could also be used to implement FEC for the payload data.
Async CRC32: Checks payload CRC to determine whether any errors have occurred. Packet is discarded if CRC fails, otherwise it is passed to higher layers.
CDC TS Correlator
This block searches for the access code/training sequence that is transmitted at the beginning of each packet. it is a modified version of GNU Radio's Correlator Estimator that computes a normalized correlation rather than an unnormalized correlation.
R[n]=\frac{\| \sum_{k=0}^{N-1} y[n+k]t^*[k]\ |^2}
{ \sqrt{ \sum_{k=0}^{N-1} \|t[k]\|^2 \sum_{k=0}^{N-1} \|y[n+k]\|^2 } }This simplifies setting of the correlation threshold as the threshold does not need to be adjusted with fluctuations in received power.
This block has the following configuration parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| symbols | Samples of the modulate training sequence. |
| threshold | Normalized correlation value required to declare training sequence found. Values typicially in range [0.0, 1.0] |
| mark delay | Offset between peak correlation sample and where output stream is tagged with various parameter estimates. Used to account for delays introduced by the matched filtering performed in the Symbol Sync block. |
Once found, this block adds the following tags to the output stream.
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
corr_start |
Marks starting sample of access code in sample stream. |
corr_est |
Marks starting sample of access code offset by mark delay. Value of tag is the normalized correlation result. |
chan_est |
Value of tag is inverse LLS channel estimate from training sequence and is used in single-tap equalisation. |
phase_est |
Value of tag is hardcoded to zero. This tag is used to reset the phase accumulation of the downstream Costas Loop block. Initial carrier phase offset is incorporated in the chan_est parameter estimate instead. |
time_est |
Value of tag is estimate of fractional symbol timing offset based on correlation result. This is used to initialize Symbol Sync's interpolation at the beginning of each packet. |
The channel estimate is a linear least squares (LLS) estimate based on the received training sequence samples.
\hat{h}_\text{LLS} = \frac{t^*}{tt^*} yThe value of \hat{h}_\text{LLS} is inverted in the chan_est tag to allow
for inverting the channel at the downstream Multiply by Tag Value block.
The fractional symbol timing offset of time_est is calculated based on the
peak correlation value and its two neighbouring samples.
\epsilon = \frac{R[n-1] + 2*R[n] + 3*R[n+1]}{R[n-1] + R[n] + R[n+1]} - 2See the block's work() method for further algorithmic implementation
details.
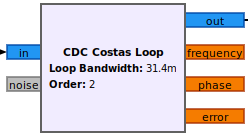
CDC Costas Loop
The CDC Costas Loop performs carrier phase and frequency tracking. The only
difference between the CDC block and the standard GNU Radio version is that
the CDC version will use bps tags found in the received symbol stream to
update the constellation used for determining the current phase error. This is
only used for payload symbols and allows the payload constellation to be
changed on a packet-by-packet basis.
See Costas Loop for details of the GNU Radio implementation.
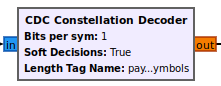
CDC Constellation Decoder
The CDC Constellation Decoder slices received symbols to constellation points
and then maps these points to their corresponding bit values. These bit values
can either be soft bits (real valued) or hard bits (0 or 1). The key
functionality of this block is that it can adapt the constellation used for
slicing based on bps tags encountered in the received symbols stream.
This block has the following configuration parameters.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Bits per Symb | Sets default symbol constellation used for slicing if no bps tag is encountered. |
| Soft Decisions | Generate soft (real valued) or hard (0 or 1) bit decisions. |
| Length Tag Name | Stream tag indicating start and length a packet's payload symbols. This block will update all tag offsets appropriately based on the bits per symbol of the constellation. |